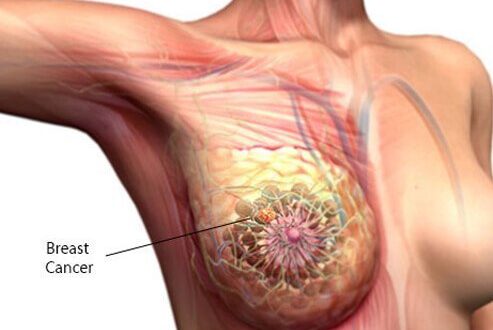
GPER activates Notch signaling in breast cancer cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) Introduction: Estrogens regulate critical signaling pathways involved in the control of cell proliferation and differentiation in reproductive and non-reproductive tissues Scarica l’articolo
Leggi tutto
 Dr. Sergio Abonante Chirurgo Senologo
Dr. Sergio Abonante Chirurgo Senologo